China's Share in Mature Process Capacity Predicted to Hit 29% in 2023, Climbing to 33% by 2027
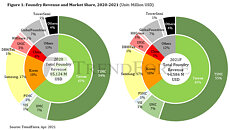
TrendForce reports that from 2023 to 2027, the global ratio of mature (>28 nm) to advanced (<16 nm) processes is projected to hover around 7:3. Propelled by policies and incentives promoting local production and domestic IC development, China's mature process capacity is anticipated to grow from 29% this year to 33% by 2027. Leading the charge are giants like SMIC, HuaHong Group, and Nexchip, while Taiwan's share is estimated to consolidate from 49% down to 42%.
Expansion predominantly targets specialty processes such as Driver ICs, CIS/ISPs, and Power Discretes, with second and third-tier Taiwanese manufacturers at the forefront
Within the Driver IC sector, the spotlight is on high voltage (HV) specialty processes. As companies aggressively pursue the 40/28 nm HV process, UMC currently dominates, trailed by GlobalFoundries. Yet, SMIC's 28HV and Nexchip's 40HV are gearing up for mass production in 4Q23 and 1H24, respectively—narrowing their technological gap with other foundries. Notably, competitors with similar process capabilities and capacities, such as PSMC, and those without twelve-inch factories like Vanguard and DBHitek, are poised to face challenges head-on in the short term. This trend may also have long-term implications for UMC and GlobalFoundries.
Expansion predominantly targets specialty processes such as Driver ICs, CIS/ISPs, and Power Discretes, with second and third-tier Taiwanese manufacturers at the forefront
Within the Driver IC sector, the spotlight is on high voltage (HV) specialty processes. As companies aggressively pursue the 40/28 nm HV process, UMC currently dominates, trailed by GlobalFoundries. Yet, SMIC's 28HV and Nexchip's 40HV are gearing up for mass production in 4Q23 and 1H24, respectively—narrowing their technological gap with other foundries. Notably, competitors with similar process capabilities and capacities, such as PSMC, and those without twelve-inch factories like Vanguard and DBHitek, are poised to face challenges head-on in the short term. This trend may also have long-term implications for UMC and GlobalFoundries.