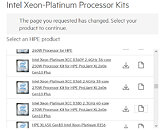
HPE Lists 40-Core Intel Ice Lake-SP Xeon Server Processor
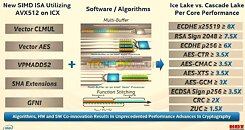
Hewlett Packard Enterprise, the company focused on making enterprise hardware and software, has today mistakenly listed some of Intel's upcoming 3rd generation Xeon Scalable processors. Called Ice Lake-SP, the latest server processor generation is expected to launch sometime in the coming days, with a possible launch date being the March 23rd "Intel Unleashed" webcast. The next generation of processors will finally bring a new vector of technologies Intel needs in server space. That means the support for PCIe 4.0 protocol for higher speed I/O and octa-channel DDR4 memory controller for much greater bandwidth. The CPU lineup will for the first time use Intel's advanced 10 nm node called 10 nm SuperFin.
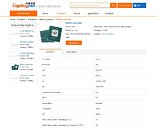
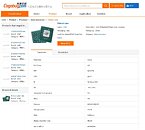
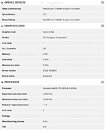
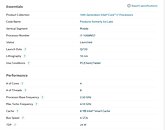
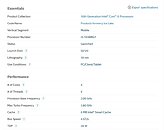
Today, in the leaked HPE listing, we get to see some of the Xeon models Intel plans to launch. Starting from 32-core models, all the way to 40-core models, all SKUs above 28 cores are supposed to use dual die configuration to achieve high core counts. The limit of a single die is 28 cores. HPE listed a few models, with the highest-end one being the Intel Xeon Platinum XCC 8380 processor. It features 40 cores with 80 threads and a running frequency of 2.3 GHz. If you are wondering about TDP, it looks like the 10 nm SuperFin process is giving good results, as the CPU is rated only for 270 Watts of power.
Today, in the leaked HPE listing, we get to see some of the Xeon models Intel plans to launch. Starting from 32-core models, all the way to 40-core models, all SKUs above 28 cores are supposed to use dual die configuration to achieve high core counts. The limit of a single die is 28 cores. HPE listed a few models, with the highest-end one being the Intel Xeon Platinum XCC 8380 processor. It features 40 cores with 80 threads and a running frequency of 2.3 GHz. If you are wondering about TDP, it looks like the 10 nm SuperFin process is giving good results, as the CPU is rated only for 270 Watts of power.