Intel Itanium Reaches End of the Road with Linux Kernel Stopping Updates
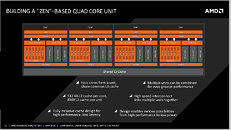
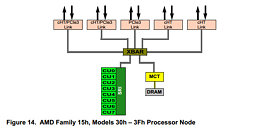
Today marks the end of support for Itanium's IA-64 architecture in the Linux kernel's 6.7 update—a significant milestone in the winding-down saga of Intel Itanium. Itanium, initially Intel's ambitious venture into 64-bit computing, faced challenges and struggled throughout its existence. It was jointly developed by Intel and HP but encountered delays and lacked compatibility with x86 software, a significant obstacle to its adoption. When AMD introduced x86-64 (AMD64) for its Opteron CPUs, which could run x86 software natively, Intel was compelled to update Xeon, based on x86-64 technology, leaving Itanium to fade into the background.
Despite ongoing efforts to sustain Itanium, it no longer received annual CPU product updates, and the last update came in 2017. The removal of IA-64 support in the Linux kernel will have a substantial impact since Linux is an essential operating system for Itanium CPUs. Without ongoing updates, the usability of Itanium servers will inevitably decline, pushing the (few) remaining Itanium users to migrate to alternative solutions, which are most likely looking to modernize their product stack.
Despite ongoing efforts to sustain Itanium, it no longer received annual CPU product updates, and the last update came in 2017. The removal of IA-64 support in the Linux kernel will have a substantial impact since Linux is an essential operating system for Itanium CPUs. Without ongoing updates, the usability of Itanium servers will inevitably decline, pushing the (few) remaining Itanium users to migrate to alternative solutions, which are most likely looking to modernize their product stack.