Intel Core i7-3610QM Tested
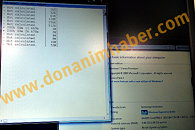
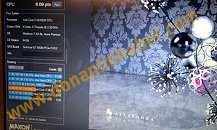
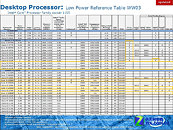
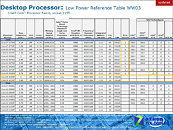
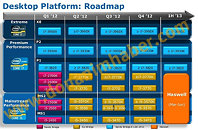
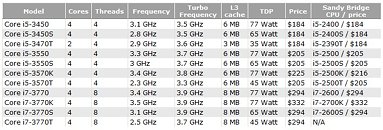
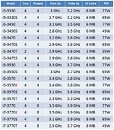
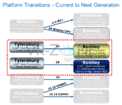
Several next-generation performance-segment notebook models across brands, will be driven by Intel's Core i7-3610QM, a quad-core chip based on the 22 nm Ivy Bridge silicon, clocked at 2.30 GHz (3.30 GHz Turbo), featuring 6 MB L3 cache. The chip features the complete instruction-set of Intel's third-generation Core processor family. DonanimHaber got to test a Samsung notebook that's based on this chip (which also uses NVIDIA GeForce GT 650M graphics), the chip was put through SuperPi 1M and 2M; and Cinebench R11. The chip crunched Pi 1M in 11.66 s, and 2M in 26.67 s. It scored 6.09 pts in Cinebench, which is a higher score than that of AMD FX-8150, DonanimHaber notes.