Intel Core i7 "Ivy Bridge-E" HEDT Processors Start Selling
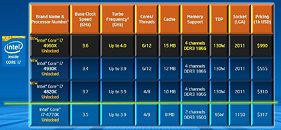
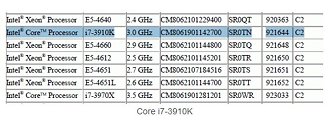
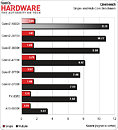
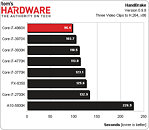
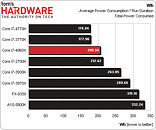
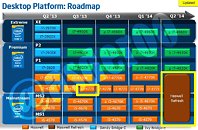
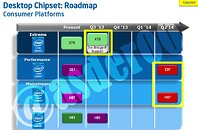
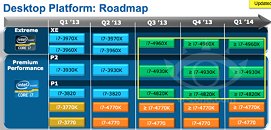
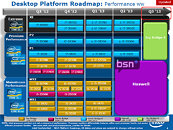
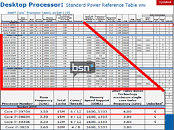
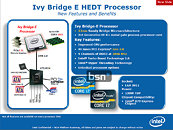
Intel made its newest Core i7 high-end desktop (HEDT) platform official with the launch of three new socket LGA2011 processors based on the swanky new 22 nm "Ivy Bridge-E" silicon. The launch includes the top-end Core i7-4960X Extreme Edition, priced at $990, followed by the Core i7-4930K at $555, and Core i7-4820K at $310. Expect a 10 percent markup across the board for these prices. Of these, the i7-4960X and i7-4930K are six-core parts, while the i7-4820K is quad-core.
The Core i7-4960X features a CPU clock speed of 3.60 GHz, with up to 4.00 GHz Turbo Boost frequency, 15 MB of L3 cache, and HyperThreading, which enables 12 logical CPUs for the OS to deal with. The i7-4930K clocks in at 3.40 GHz, with up to 3.90 GHz Turbo Boost, 12 MB of L3 cache, and HyperThreading. The i7-4820K, at its price point, can be extremely inviting for people with their minds set on a Core i7-4770K. It features 3.70 GHz clocks with up to 3.90 GHz Turbo Boost, 10 MB of L3 cache, and HyperThreading, enabling 8 logical CPUs. All three parts feature quad-channel DDR3 integrated memory controller with native support for DDR3-1866, 48-lane PCI-Express gen 3.0 root complexes, and 130W rated TDPs.
The Core i7-4960X features a CPU clock speed of 3.60 GHz, with up to 4.00 GHz Turbo Boost frequency, 15 MB of L3 cache, and HyperThreading, which enables 12 logical CPUs for the OS to deal with. The i7-4930K clocks in at 3.40 GHz, with up to 3.90 GHz Turbo Boost, 12 MB of L3 cache, and HyperThreading. The i7-4820K, at its price point, can be extremely inviting for people with their minds set on a Core i7-4770K. It features 3.70 GHz clocks with up to 3.90 GHz Turbo Boost, 10 MB of L3 cache, and HyperThreading, enabling 8 logical CPUs. All three parts feature quad-channel DDR3 integrated memory controller with native support for DDR3-1866, 48-lane PCI-Express gen 3.0 root complexes, and 130W rated TDPs.