Hogwarts Legacy Gets a New Big Patch
Avalanche Software has released the latest March 8 patch for Hogwarts Legacy, that fixes various bugs and improves gameplay, performance, and stability. The extensive update also includes fixes for online, gameplay, audio, UI, cinematics, ray tracing, save game, display and miscellaneous issues.
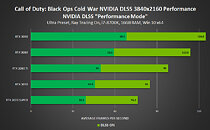
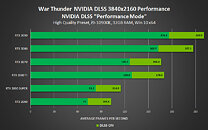
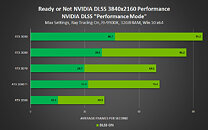
The changelog includes major reworks, from patching out memory leaks, improved VRAM usage, to VFX crashes, lighting optimizations with NVIDIA drivers, improved stability and performance with ray tracing, directional light shadows and shadows on trees with ray tracing, various Ansel issues, and plenty of gameplay issues, including missions, broom flight, world events, and characters. The new patch also updates the minimum Nvidia and AMD graphics driver recommendations, which could be directly connected to the improved VRAM usage, as the game was easily going over 14 GB with RT enabled on 1080p, 1440p, and 2160p resolutions.
The changelog includes major reworks, from patching out memory leaks, improved VRAM usage, to VFX crashes, lighting optimizations with NVIDIA drivers, improved stability and performance with ray tracing, directional light shadows and shadows on trees with ray tracing, various Ansel issues, and plenty of gameplay issues, including missions, broom flight, world events, and characters. The new patch also updates the minimum Nvidia and AMD graphics driver recommendations, which could be directly connected to the improved VRAM usage, as the game was easily going over 14 GB with RT enabled on 1080p, 1440p, and 2160p resolutions.