GIGABYTE Z490 Motherboards to Support 11th Gen Core Processors
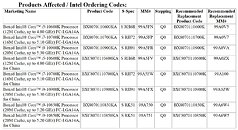
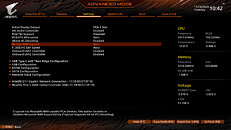
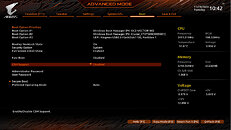
GIGABYTE TECHNOLOGY Co. Ltd, a leading manufacturer of motherboards, graphics cards, and hardware solutions, today announced that all Z490 motherboards featuring PCIe 4.0 hardware design can support the 11th Gen. Intel Core processors perfectly by update to the latest F20 BIOS, and provide the extreme bandwidth and performance for PCIe 4.0 graphics cards and SSDs. With a snap update of the latest BIOS from GIGBAYTE's official site, users can enjoy the full pack of advantages and unlock the Resizable BAR function on GIGABYTE Z490 and H470 motherboards.
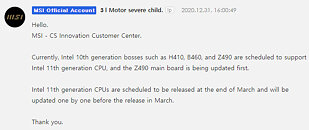
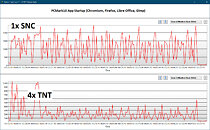
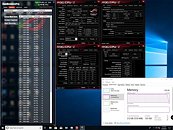
The latest 11th Gen. Intel Core processors will be launched on March 2021. The new processors keep the same architecture as the previous generation but they enable the PCIe 4.0 support, which meet a range of needs for users who expect broad bandwidth and super high transfer speed of PCIe 4.0 on the Intel platform. For those who own one of the current generation motherboards, it would be a great deal to enjoy the performance uplift on Z490 motherboards with PCIe 4.0 function and 11th Gen. Intel Core processors support.
The latest 11th Gen. Intel Core processors will be launched on March 2021. The new processors keep the same architecture as the previous generation but they enable the PCIe 4.0 support, which meet a range of needs for users who expect broad bandwidth and super high transfer speed of PCIe 4.0 on the Intel platform. For those who own one of the current generation motherboards, it would be a great deal to enjoy the performance uplift on Z490 motherboards with PCIe 4.0 function and 11th Gen. Intel Core processors support.