GIGABYTE Adds Ryzen 7 5800X3D Support, Unlocks Max CPU Boost Clock Override
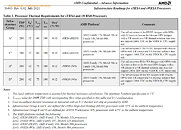
GIGABYTE over the last week posted UEFI firmware updates for its Socket AM4 motherboards that add support for the upcoming AMD Ryzen 5800X3D processor. Released for motherboards across its AMD 400-series and 500-series lineups; the updates pack AGESA ComboPI V2 1.2.0.6 Patch-b microcode. Another key feature of these updates are that they re-introduce the "Max CPU Boost Clock Override" toggle, which appears when a Ryzen 5000 "Vermeer" processor is installed.
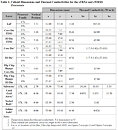
The Ryzen 7 5800X3D is an 8-core/16-thread processor based on the "Zen 3" microarchitecture, and packs the AMD 3D Vertical Cache (3DV Cache) technology, featuring 100 MB of Total Cache (AMD jargon for the sum of all L2 + L3 cache). The company claims gaming performance on par with the Core i9-12900K "Alder Lake" processor. The re-introduction of the Boost Frequency overrides signal that the company wants enthusiasts to go to town with overclocking, making this a possible response to the i9-12900KS gaming performance, at a lower price-point.
The Ryzen 7 5800X3D is an 8-core/16-thread processor based on the "Zen 3" microarchitecture, and packs the AMD 3D Vertical Cache (3DV Cache) technology, featuring 100 MB of Total Cache (AMD jargon for the sum of all L2 + L3 cache). The company claims gaming performance on par with the Core i9-12900K "Alder Lake" processor. The re-introduction of the Boost Frequency overrides signal that the company wants enthusiasts to go to town with overclocking, making this a possible response to the i9-12900KS gaming performance, at a lower price-point.