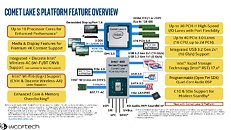
Intel Enthusiast-Grade K Processors in the Comet Lake-S Family Rumored to Feature 125 W TDP
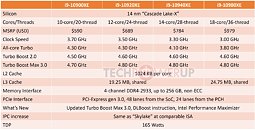
This piece of news shouldn't surprise anyone, except for the fact that Intel is apparently signing on a TDP of 125 W for even its K-series unlocked processors for their next-generation Comet Lake-S family. Intel's current Comet Lake 9900K CPU features a TDP of "only" 95 W - when compared to the rumored 125 W of the 10900K), whilst their current top offering, the i9-9900KS, features a 127 W TDP. Remember that Intel's 10900K should feature 10 cores and 20 threads, two extra cores than their current 9900K - this should explain the increased TDP, a mathematical necessity given that Intel can only count on marginal improvements to its 14 nm fabrication process to frequencies and power consumption of its CPUs.
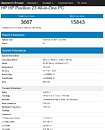
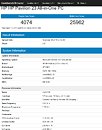
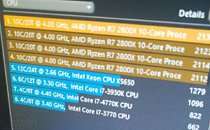
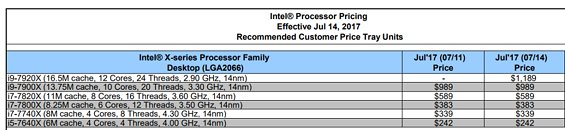
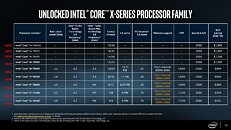
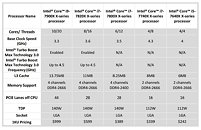
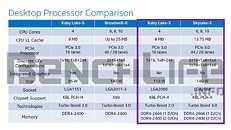
A leaked slide from momomo on Twitter shows, if real, that Intel's future enthusiast-grade CPUs (likely i5-10600K, i7-10700K and i9-10900K) will feature this 125 W TDP, while other launches in that family will make do with the more traditional 65 W TDP (interesting to see that Intel has some 10-core CPUs with 65 W TDP, the same as their current 9900, despite two more cores). A footnote on the leaked slide shows that these K processors can be configured for a 95 W TDP, but this would likely come at a significant cost to operating frequency. Intel seems to be bringing a knife to a gunfight (in terms of core counts and TDP) with AMD's Ryzen 3000 and perhaps Ryzen 4000 CPUs, should those and Intel's future offerings actually coexist in the market.
A leaked slide from momomo on Twitter shows, if real, that Intel's future enthusiast-grade CPUs (likely i5-10600K, i7-10700K and i9-10900K) will feature this 125 W TDP, while other launches in that family will make do with the more traditional 65 W TDP (interesting to see that Intel has some 10-core CPUs with 65 W TDP, the same as their current 9900, despite two more cores). A footnote on the leaked slide shows that these K processors can be configured for a 95 W TDP, but this would likely come at a significant cost to operating frequency. Intel seems to be bringing a knife to a gunfight (in terms of core counts and TDP) with AMD's Ryzen 3000 and perhaps Ryzen 4000 CPUs, should those and Intel's future offerings actually coexist in the market.